Which polynomial lists the powers in descending order – Polynomials, mathematical expressions composed of terms arranged in descending order of their exponents, play a pivotal role in various mathematical operations and real-world applications. This guide delves into the intricacies of polynomials, exploring their structure, representation, mathematical operations, and practical applications, providing a comprehensive understanding of this fundamental algebraic concept.
Polynomial Terms

A polynomial is a mathematical expression consisting of one or more terms. Each term is a product of a constant coefficient and a variable raised to a non-negative integer power.
A polynomial term is written in the form ax^n, where ais the coefficient, xis the variable, and nis the exponent or power.
Polynomials with terms in descending order have the highest power term first, followed by the next highest power term, and so on, until the constant term (which has an exponent of 0).
Examples, Which polynomial lists the powers in descending order
- x^3- 2x^2 + 5x – 1
- 3x^4- x^3 + 2x^2 – 5
- -2x^5 + 4x^3- x^2 + 7x – 10
Polynomial Representation
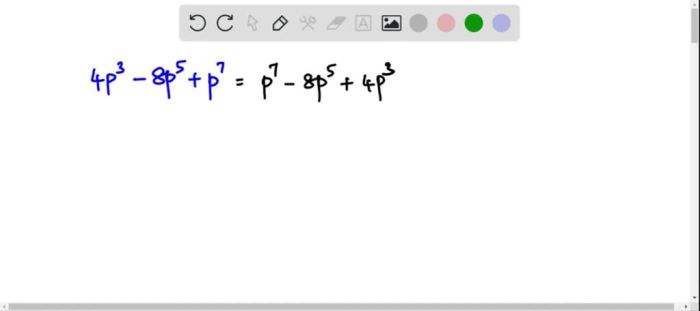
Polynomials can be represented in various ways, including:
- Standard form: a_nx^n + a_n-1x^n-1 + … + a_1x + a_0, where a_nis the coefficient of the highest power term.
- Factored form: (x- r_1)(x – r_2)…(x – r_k) , where r_1, r_2, …, r_kare the roots of the polynomial.
- Expanded form: ax^n + bx^n-1 + … + px + q, where a, b, …, p, qare the coefficients of the polynomial.
Listing powers in descending order is significant because it allows for easier comparison and manipulation of polynomials.
Examples, Which polynomial lists the powers in descending order
- Standard form: x^3- 2x^2 + 5x – 1
- Factored form: (x- 1)(x – 2)(x + 1)
- Expanded form: x^3- x^2 – 2x + 2
Mathematical Operations

Mathematical operations on polynomials, such as addition, subtraction, and multiplication, can be performed by combining like terms and adjusting the powers accordingly.
When adding or subtracting polynomials, the terms with the same power are grouped together, and the coefficients are added or subtracted.
When multiplying polynomials, the terms of one polynomial are multiplied by each term of the other polynomial, and the powers are added.
Examples, Which polynomial lists the powers in descending order
- Addition: (x^2 + 2x- 3) + (x^2 – x + 1) = 2x^2 + x – 2
- Subtraction: (x^3- 2x^2 + 5x – 1) – (x^2 – x + 1) = x^3 – 3x^2 + 6x – 2
- Multiplication: (x^2 + 2x- 3)(x – 1) = x^3 + x^2 – 5x + 3
Applications of Descending Order
Polynomials with powers in descending order are useful in various applications, including:
- Curve fitting: Approximating data points with a polynomial function.
- Integration and differentiation: Simplifying calculations involving integrals and derivatives.
- Modeling real-world phenomena: Describing relationships between variables in physics, chemistry, and economics.
Descending order simplifies calculations and analysis by allowing for easier manipulation and comparison of terms.
Examples, Which polynomial lists the powers in descending order
- Curve fitting: Using a quadratic polynomial ( ax^2 + bx + c) to approximate a set of data points.
- Integration: Integrating a polynomial function x^3 + 2x^2- 5x + 1 to obtain (x^4)/4 + (2x^3)/3- (5x^2)/2 + x + C .
- Modeling: Using a polynomial function to describe the trajectory of a projectile, where the coefficients represent physical parameters such as velocity and acceleration.
Polynomial Evaluation
Evaluating a polynomial involves substituting a specific value for the variable and simplifying the expression.
The order of powers affects polynomial evaluation because the powers determine the order in which the terms are evaluated.
Examples, Which polynomial lists the powers in descending order
- Evaluating x^2- 2x + 1 at x = 2: (2)^2- 2(2) + 1 = 1
- Evaluating x^3- x^2 + 2x – 5 at x =-1 : (-1)^3- (-1)^2 + 2(-1) – 5 = -7
- Evaluating 2x^4- 3x^3 + 5x^2 – 7x + 10 at x = 1: 2(1)^4- 3(1)^3 + 5(1)^2 – 7(1) + 10 = 6
Answers to Common Questions: Which Polynomial Lists The Powers In Descending Order
What is the significance of listing powers in descending order in polynomials?
Arranging powers in descending order simplifies polynomial operations, such as addition, subtraction, and multiplication, and facilitates polynomial evaluation at specific values.
How does the order of powers affect polynomial evaluation?
The order of powers determines the sequence in which terms are evaluated, influencing the final result of the polynomial evaluation.
What are some practical applications of polynomials with powers in descending order?
Polynomials in descending order find applications in modeling physical phenomena, such as projectile motion and fluid dynamics, and in solving optimization problems in engineering and economics.