How might an athlete’s vital capacity compare to a non-athlete? This intriguing question delves into the realm of respiratory physiology, exploring the remarkable differences between the lungs of those who engage in strenuous physical activity and those who do not.
Join us as we embark on a journey to uncover the fascinating truth behind this physiological disparity.
Vital capacity, a crucial measure of lung function, plays a pivotal role in athletic performance. Athletes, with their finely tuned respiratory systems, possess a significantly higher vital capacity compared to non-athletes. This enhanced lung capacity enables them to meet the increased oxygen demands of intense exercise, providing the fuel necessary for optimal performance.
Respiratory System of Athletes
The respiratory system is a complex network of organs that work together to facilitate the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide between the body and the environment. In athletes, the respiratory system plays a crucial role in providing the body with the oxygen it needs to sustain high levels of physical activity.
The respiratory system consists of the lungs, airways, and muscles that control breathing. The lungs are responsible for gas exchange, where oxygen from the air is taken into the bloodstream and carbon dioxide is released. The airways, including the trachea, bronchi, and bronchioles, provide a passage for air to flow in and out of the lungs.
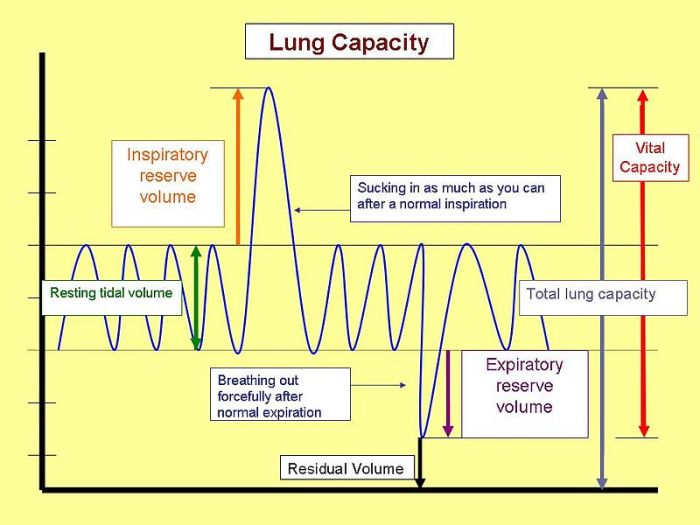
The muscles of respiration, such as the diaphragm and intercostal muscles, contract and relax to control the volume and rate of breathing.Athletes have a higher vital capacity compared to non-athletes due to several factors. First, athletes typically have larger lung volumes.
This is because they have increased lung capacity through regular exercise, which causes the muscles of respiration to become stronger and more efficient. Second, athletes have a higher breathing rate than non-athletes, which allows them to take in more oxygen and expel more carbon dioxide.
Finally, athletes have a lower residual volume, which is the amount of air remaining in the lungs after exhalation. This allows them to start with a higher lung volume and take in more oxygen with each breath.
Vital Capacity and Its Significance
Vital capacity is the maximum volume of air that can be exhaled after a maximal inspiration. It is an important measure of lung function and is often used to assess the overall health of the respiratory system. Vital capacity is also an important factor in athletic performance, as it determines the amount of oxygen that can be delivered to the muscles during exercise.
Athletes with a higher vital capacity have a greater ability to sustain high levels of physical activity and perform at their best.For example, in endurance sports such as running and cycling, a higher vital capacity allows athletes to maintain a higher oxygen uptake for a longer period of time.
This means they can run or cycle for longer distances without becoming fatigued. In power sports such as weightlifting and sprinting, a higher vital capacity allows athletes to generate more force and power. This is because they can deliver more oxygen to their muscles, which in turn allows them to produce more energy.
Factors Influencing Vital Capacity

Several factors influence vital capacity, including genetics, training, and environmental factors.Genetics: Vital capacity is partly determined by genetics. Some people are simply born with larger lungs and stronger respiratory muscles than others. However, training can also play a role in increasing vital capacity.Training:
Regular exercise can increase vital capacity by strengthening the muscles of respiration and increasing the size of the lungs. This is because exercise causes the body to demand more oxygen, which in turn stimulates the respiratory system to adapt and become more efficient.Environmental
factors: Environmental factors such as altitude can also affect vital capacity. At higher altitudes, the air is thinner and contains less oxygen. This can lead to a decrease in vital capacity, as the body must work harder to extract oxygen from the air.
Training Methods to Enhance Vital Capacity

There are several training methods that can be used to enhance vital capacity. These methods include:Aerobic exercise: Aerobic exercise, such as running, cycling, and swimming, is an effective way to increase vital capacity. This is because aerobic exercise causes the body to demand more oxygen, which in turn stimulates the respiratory system to adapt and become more efficient.Interval
training: Interval training is a type of training that involves alternating between periods of high-intensity exercise and rest. Interval training can be an effective way to increase vital capacity, as it forces the body to work harder and recover quickly.Breathing
exercises: Breathing exercises, such as diaphragmatic breathing and pursed-lip breathing, can also help to increase vital capacity. These exercises help to strengthen the muscles of respiration and improve the efficiency of breathing.
Measuring Vital Capacity
Vital capacity can be measured using a variety of techniques. The most common method is spirometry, which involves breathing into a tube connected to a spirometer. The spirometer measures the volume of air exhaled and can be used to calculate vital capacity.Other
methods of measuring vital capacity include body plethysmography and helium dilution. Body plethysmography involves sitting in a sealed chamber and breathing into a mouthpiece. The pressure changes in the chamber are used to calculate vital capacity. Helium dilution involves breathing a mixture of helium and oxygen and then measuring the concentration of helium in the exhaled air.
The concentration of helium can be used to calculate vital capacity.
Implications for Athletic Performance: How Might An Athlete’s Vital Capacity Compare To A Non-athlete
Vital capacity has a significant impact on athletic performance. Athletes with a higher vital capacity have a greater ability to sustain high levels of physical activity and perform at their best. This is because they can deliver more oxygen to their muscles, which in turn allows them to produce more energy.For
example, in endurance sports such as running and cycling, a higher vital capacity allows athletes to maintain a higher oxygen uptake for a longer period of time. This means they can run or cycle for longer distances without becoming fatigued.
In power sports such as weightlifting and sprinting, a higher vital capacity allows athletes to generate more force and power. This is because they can deliver more oxygen to their muscles, which in turn allows them to produce more energy.
Essential FAQs
How does vital capacity affect athletic performance?
Vital capacity plays a crucial role in athletic performance by providing the necessary oxygen to fuel muscles during intense exercise. A higher vital capacity allows athletes to sustain higher levels of activity for longer durations.
What factors influence vital capacity?
Vital capacity is influenced by a combination of genetic, environmental, and training factors. Genetics play a role in determining the size and shape of the lungs, while training can significantly increase vital capacity through exercises that strengthen respiratory muscles and improve lung elasticity.
How can athletes improve their vital capacity?
Athletes can improve their vital capacity through various training methods, including interval training, endurance training, and respiratory muscle training. These methods aim to increase the strength and endurance of the respiratory muscles, allowing for deeper and more efficient breathing.